Geometric Abstraction: Forms and Innovations in Art
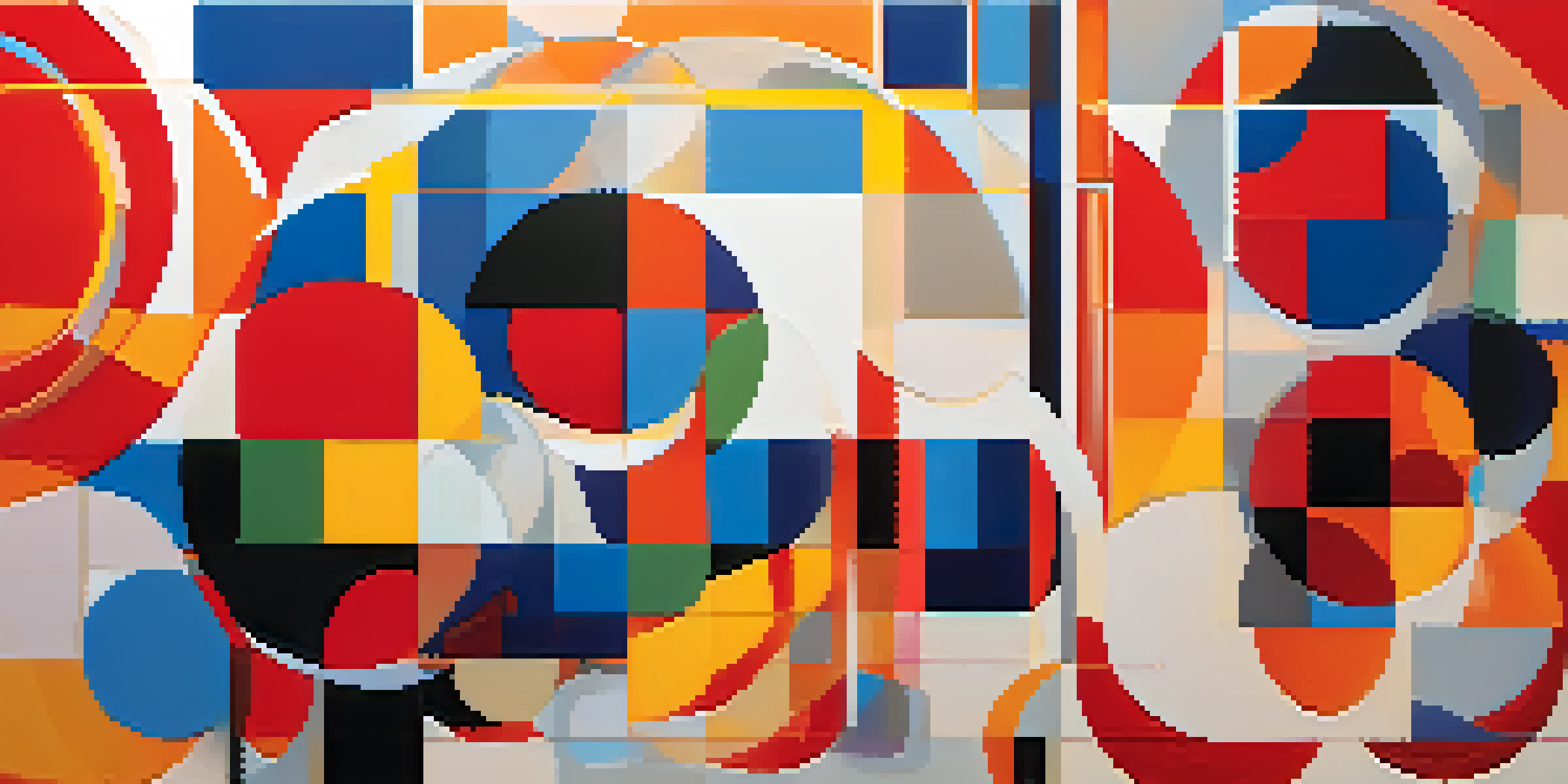

Understanding Geometric Abstraction in Art
Geometric abstraction is an art movement that emerged in the early 20th century, focusing on the use of simple geometric forms like squares, circles, and triangles. This style emphasizes the purity of shapes and colors, stripping away representational elements to highlight the beauty in simplicity. Artists sought to convey emotions and ideas through these forms, allowing viewers to interpret art in a more personal and subjective manner.
The broader art scene is always inspired by geometric abstraction, revealing the beauty in simplicity and form.
One of the key figures in geometric abstraction is Kazimir Malevich, known for his iconic 'Black Square' painting, which challenged traditional perspectives on art. This movement laid the groundwork for future artistic innovations, pushing boundaries and encouraging artists to rethink the role of form and color. By prioritizing geometry, artists aimed to create a universal language that transcended cultural and linguistic differences.
As geometric abstraction evolved, it influenced numerous other movements, including Minimalism and Op Art. These styles continued to explore the relationships between form, color, and perception, highlighting the dynamic interplay between art and viewer experience. In this way, geometric abstraction not only transformed artistic expression but also reflected broader societal changes during its time.
Historical Context of Geometric Abstraction
The roots of geometric abstraction can be traced back to the early 20th century, coinciding with significant social and political changes worldwide. Artists were responding to the rapid advancements in technology and the shifting cultural landscape, seeking new ways to express their ideas. Movements like Cubism and Futurism laid the groundwork for geometric abstraction by breaking down forms into their basic components.
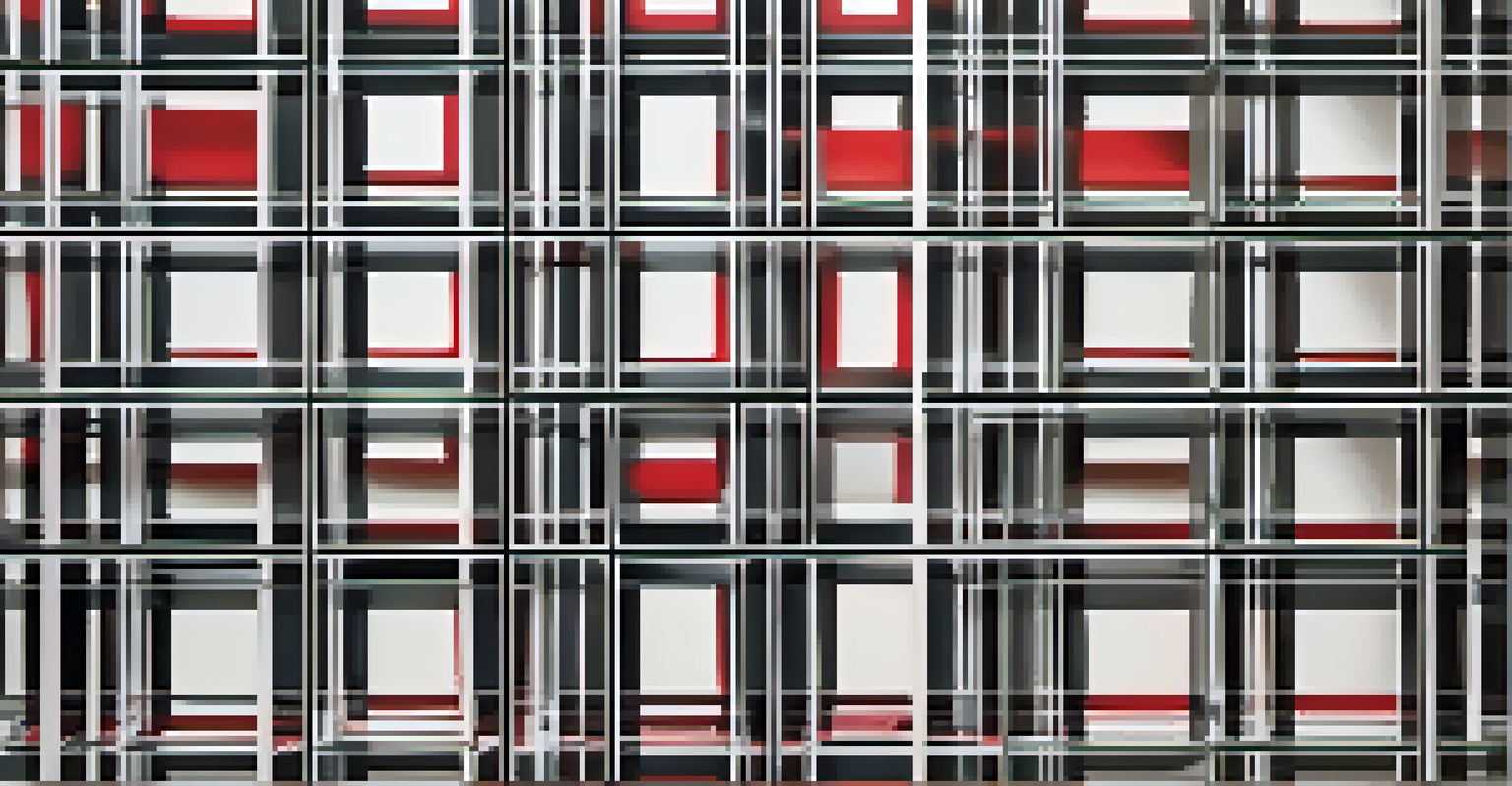
In the wake of World War I, artists like Piet Mondrian sought to create a sense of order and harmony through geometric forms. His work emphasized the use of primary colors and straight lines, reflecting a desire for stability in a chaotic world. This period marked a turning point in art history, as artists began to embrace abstraction as a means of exploration rather than representation.
Geometric Abstraction Defined
This art movement focuses on simple geometric forms, emphasizing purity and personal interpretation.
The influence of geometric abstraction extended beyond visual arts, impacting architecture and design as well. Architects like Le Corbusier adopted geometric principles in their designs, promoting functionality and simplicity. This interconnectedness between art and other disciplines showcases the movement's far-reaching impact and enduring legacy.
Key Artists and Their Contributions
Several artists have played pivotal roles in the development of geometric abstraction, each contributing their unique perspective. Kazimir Malevich, as mentioned earlier, is renowned for his radical approach to abstraction, while Piet Mondrian's emphasis on grid patterns and primary colors solidified his status as a pioneer. Their works continue to inspire new generations of artists and shape contemporary art practices.
Art is a universal language that transcends cultural boundaries, and geometric abstraction speaks to this truth.
Another influential figure is Theo van Doesburg, who co-founded De Stijl, a movement that embraced geometric abstraction in both painting and architecture. His innovative use of color and form challenged conventional artistic norms and encouraged collaboration among artists and architects. Van Doesburg's work exemplifies the interconnectedness of artistic disciplines during this period.
Additionally, artists like Frank Stella and Donald Judd further pushed the boundaries of geometric abstraction in the mid-20th century. Their creations often incorporated three-dimensional elements, blurring the lines between painting and sculpture. This evolution demonstrates the versatility and adaptability of geometric abstraction as it continues to inspire artists today.
Techniques and Materials in Geometric Abstraction
The techniques and materials used in geometric abstraction have played a significant role in shaping its visual language. Artists often employed precise methods to create clean lines and sharp angles, utilizing tools like rulers and compasses for accuracy. This meticulous approach reflects a commitment to the principles of order and structure that define the movement.
In terms of materials, geometric abstraction has embraced a wide range of mediums, from traditional oil paints to more experimental materials like acrylics and metal. This versatility allows artists to explore different textures and finishes, enhancing the visual impact of their work. For instance, the use of bold colors in acrylics can create a vibrant, dynamic effect that captures the viewer's attention.
Historical Significance
Geometric abstraction emerged in response to early 20th-century societal changes, influencing various art and design movements.
Moreover, the rise of digital art has introduced new possibilities for geometric abstraction. Artists can now manipulate shapes and colors with precision using software, expanding the boundaries of what geometric abstraction can achieve. This fusion of traditional techniques with modern technology showcases the movement's adaptability and relevance in today's art world.
Geometric Abstraction in Contemporary Art
Today, geometric abstraction continues to thrive in contemporary art, influencing a diverse range of artists across the globe. Many contemporary artists draw inspiration from the movement, incorporating geometric forms into their work while experimenting with new materials and techniques. This evolution reflects the ongoing dialogue between past and present in the art world.
Artists like Julie Mehretu and Sarah Morris have gained recognition for their innovative approaches to geometric abstraction, often blending elements of abstraction with narrative and social commentary. Their works challenge viewers to consider the relationship between form and content, inviting deeper engagement with the art. This blend of tradition and contemporary themes keeps the movement fresh and relevant.
Moreover, geometric abstraction has found its way into public art installations and urban environments, transforming spaces and engaging communities. These large-scale works often utilize bold colors and patterns, creating visually striking experiences for passersby. This accessibility reinforces the idea that geometric abstraction is not just confined to galleries but can also be a part of everyday life.
The Impact of Geometric Abstraction on Design
Geometric abstraction has had a profound impact on design, influencing everything from graphic design to interior decor. The clean lines and simple shapes characteristic of this movement have become staples in modern design aesthetics. Designers often draw on geometric principles to create visually appealing and functional products that resonate with contemporary sensibilities.
In graphic design, geometric shapes are frequently used to create logos, advertisements, and digital interfaces. This reliance on geometric forms allows for clarity and instant recognition, making it an effective tool for brands seeking to convey their identity. The use of color and form in design often mirrors the principles established by geometric abstraction, showcasing its lasting influence.
Contemporary Relevance
Today, geometric abstraction continues to inspire artists and designers, merging traditional techniques with modern technologies.
Furthermore, the principles of geometric abstraction are evident in architecture, where buildings often incorporate geometric patterns and shapes for both structural and aesthetic purposes. This harmonious blend of form and function creates spaces that inspire and engage inhabitants. As a result, geometric abstraction continues to shape not only visual art but also the world around us.
The Future of Geometric Abstraction in Art
As we look to the future, geometric abstraction shows no signs of fading away; rather, it is evolving and adapting to new contexts and technologies. Artists are exploring innovative ways to incorporate geometric forms into their work, often merging traditional practices with cutting-edge techniques. This ongoing experimentation highlights the movement's resilience and relevance in a rapidly changing art landscape.
The rise of virtual reality and augmented reality presents exciting opportunities for geometric abstraction, allowing artists to create immersive experiences that engage viewers in new ways. These technologies enable the exploration of space and form in ways that were previously unimaginable, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression. This intersection of art and technology is likely to shape the future of geometric abstraction significantly.

Moreover, the movement's emphasis on simplicity and clarity resonates with contemporary audiences seeking meaningful connections in a complex world. As artists continue to explore the language of geometric abstraction, they will undoubtedly find fresh avenues for expression, ensuring that this influential movement remains a vital part of the art world for years to come.